Bearings, a key component in industrial equipment, play a central role in many devices that involve rotation, linear movement or load bearing. They play a decisive role in reducing friction, improving efficiency, increasing equipment durability and ensuring the stability of mechanical operation. The following will outline the use of bearings in different industrial equipment according to their role and purpose:
Electric devices and power generation equipment
Function:
- Reducing friction: Bearings support rotating and fixed parts, significantly reducing mechanical friction, ensuring smooth rotation, thereby improving efficiency.
- Improving efficiency: Without bearings, rotating parts will generate a lot of friction and heat, reducing energy efficiency. Bearings help improve performance.
- Increasing durability: By reducing wear on rotating parts, bearings can extend the service life of electric devices and power generation equipment.
Use examples:
- Rolling bearings: Commonly used to support the rotating parts of electric devices and reduce friction.
- Sliding bearings: Suitable for large or high-power equipment, providing more stable support.
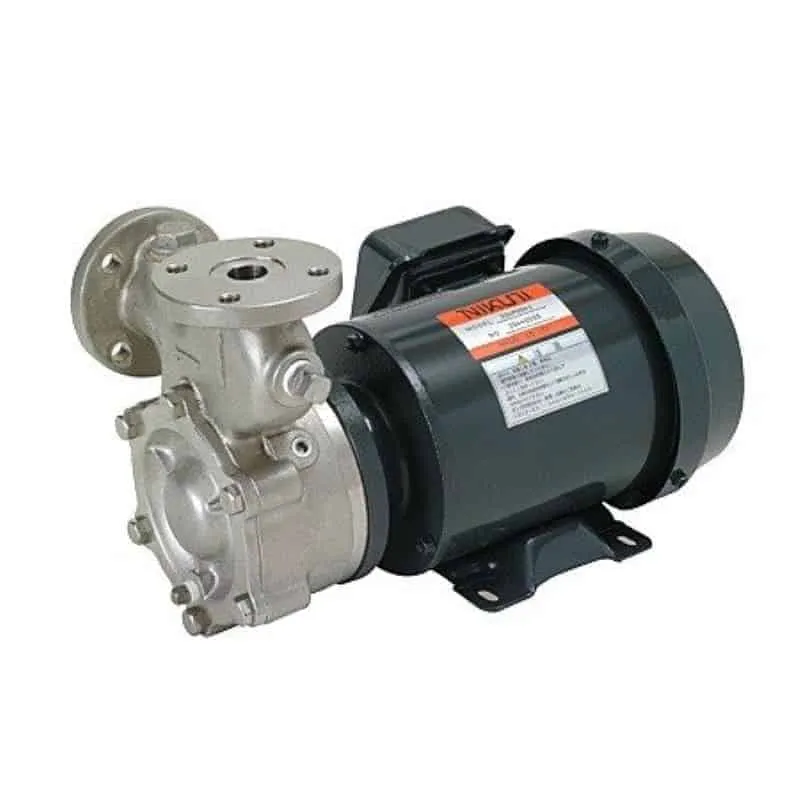
Pumps and compression devices
Function:
- Support rotation: Bearings ensure smooth operation of equipment by supporting the rotating shaft.
- Bearing loads: They can withstand the challenges of high pressure and high-speed flow in industrial applications.
- Enhanced sealing: High-quality bearings with appropriate seals can effectively reduce oil or gas leakage.
Use cases:
- Rolling bearings: Commonly used to handle radial and axial loads.
- Self-lubricating bearings: Especially suitable for harsh environments and reduce maintenance requirements.

Power transmission systems (gears, chains, belts)
Function:
- Transmit power: Bearings enable gears, sprockets and pulleys to run smoothly.
- Reduce wear: They reduce friction between moving parts and improve system efficiency.
Use cases:
- Rolling bearings: Used in gearboxes, common types are deep groove ball or cylindrical roller bearings.
- Needle roller bearings: Suitable for compact designs with limited space.
Processing equipment (lathes, milling machines, grinders)
Function:
- Improve precision: Bearings support high-precision components and ensure machining accuracy.
- Bearing loads: They withstand axial and radial forces generated by cutting operations.
- Reduce vibration: High-precision bearings can effectively reduce vibration and improve machining quality.
Use cases:
- High-precision bearings: Common examples include angular contact ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings.
- Super-precision bearings: Used in advanced CNC machine tools with extremely high precision.
Conveyor equipment (conveyor belts, chain systems)
Funktionen:
- Reduce friction: Bearings ensure smooth operation of rollers and chains.
- Support loads: They bear the weight of materials, especially in heavy-duty systems.
- Increase durability: Bearings enhance the stability and service life of conveyor systems.
Use cases:
- Roller bearings: Support conveyor belt rollers, allowing them to rotate smoothly.
- Needle bearings: Used in high-load, space-constrained applications.
Zusammenfassung:
Bearings play an integral role in industrial equipment and are essential for reducing friction, improving efficiency, increasing equipment durability, and ensuring precision. Selecting the right bearings and properly maintaining them is critical to ensuring the reliability and longevity of industrial equipment, and the specific selection should be based on load, speed, and environmental conditions. Proper use of bearings not only improves performance, but also reduces operating costs.
