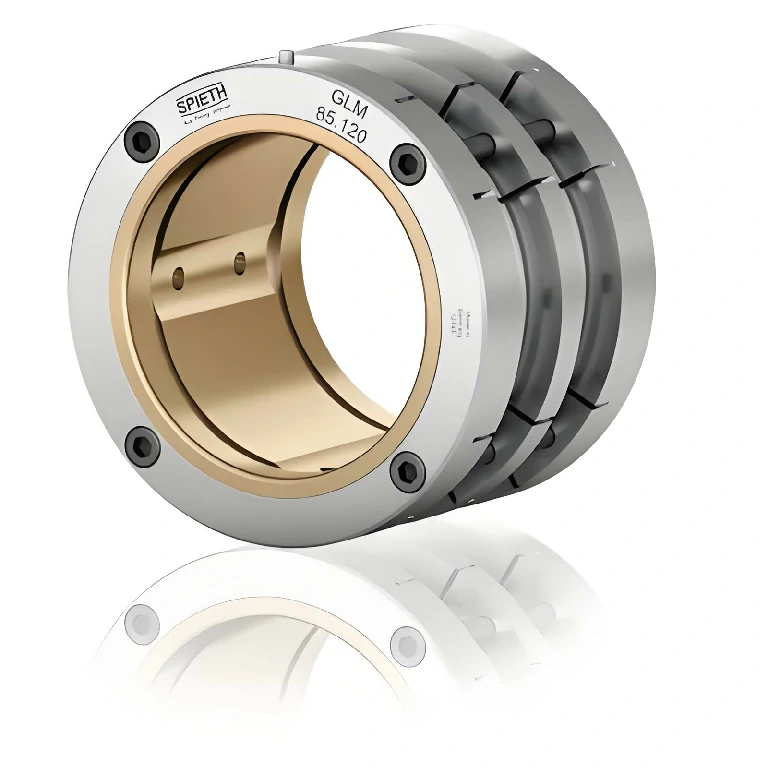
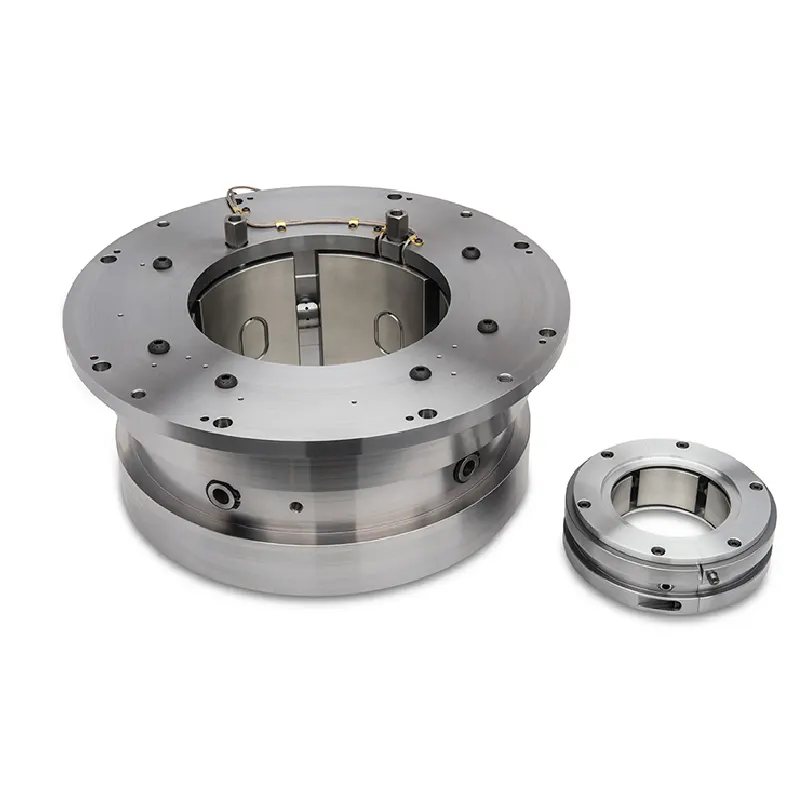
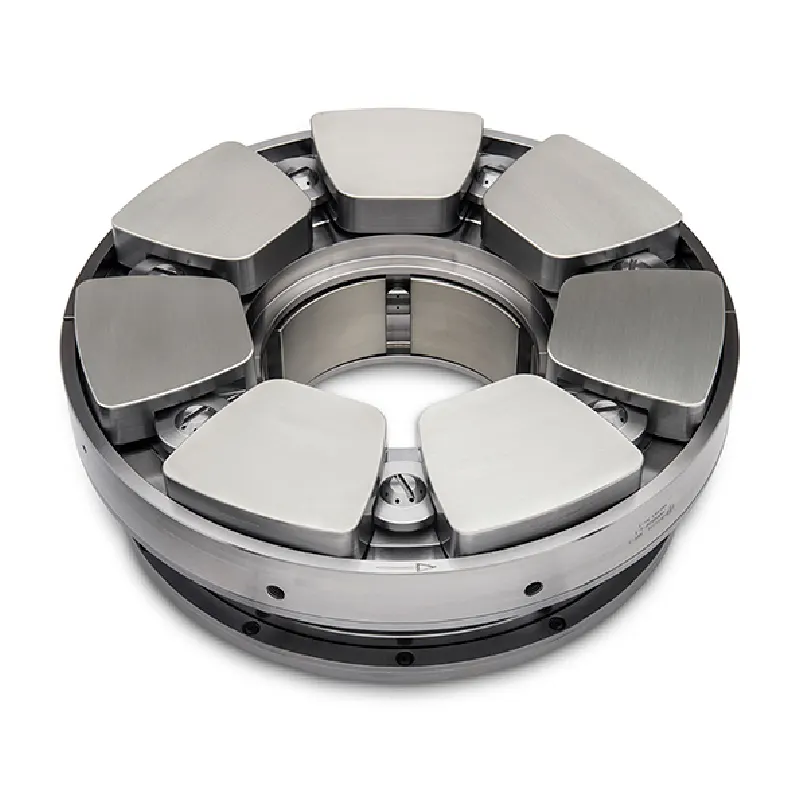
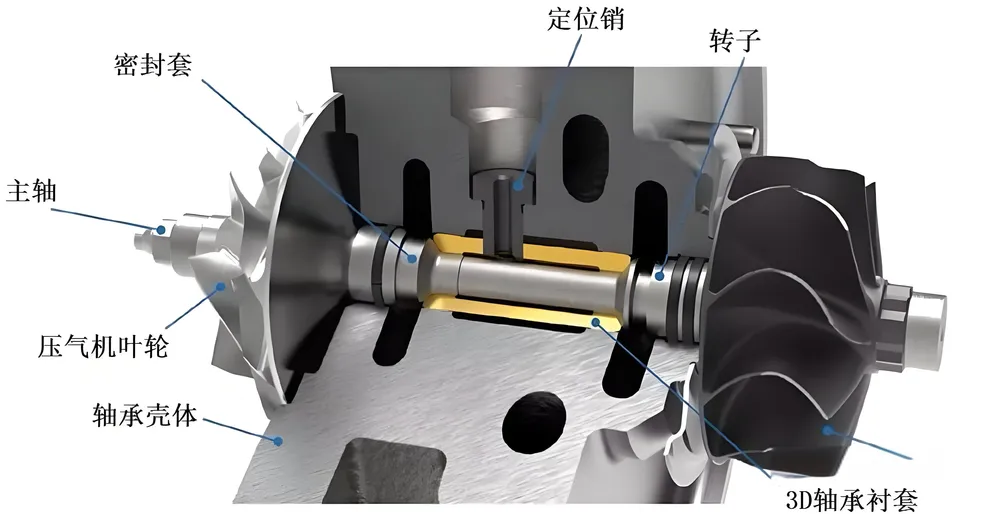
Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing
Main features of Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing
- Working principle: The rotation of the shaft generates pressure in the lubricant to support external loads.
- Structural design: No rolling elements are required, relying entirely on fluid dynamics.
- Non-contact operation: There is always a fluid film between the shaft and the bearing surface to avoid direct contact.
Core advantages
- Low friction performance
- High precision support
- Smooth operation
- Strong durability
- Wide adaptability
Wprowadzenie
Radial hydrodynamic bearing is a sliding bearing that relies on the relative movement between the journal and the bearing to form a hydrodynamic lubrication film to bear radial loads. Its working principle is to use the dynamic pressure effect of the lubricant (usually oil) generated when the journal rotates to form a stable lubrication film, thereby reducing friction and wear. This type of bearing has the advantages of strong load-bearing capacity, stable operation, and long life, and is widely used in industrial equipment, energy industry, transportation, precision machinery and other fields.
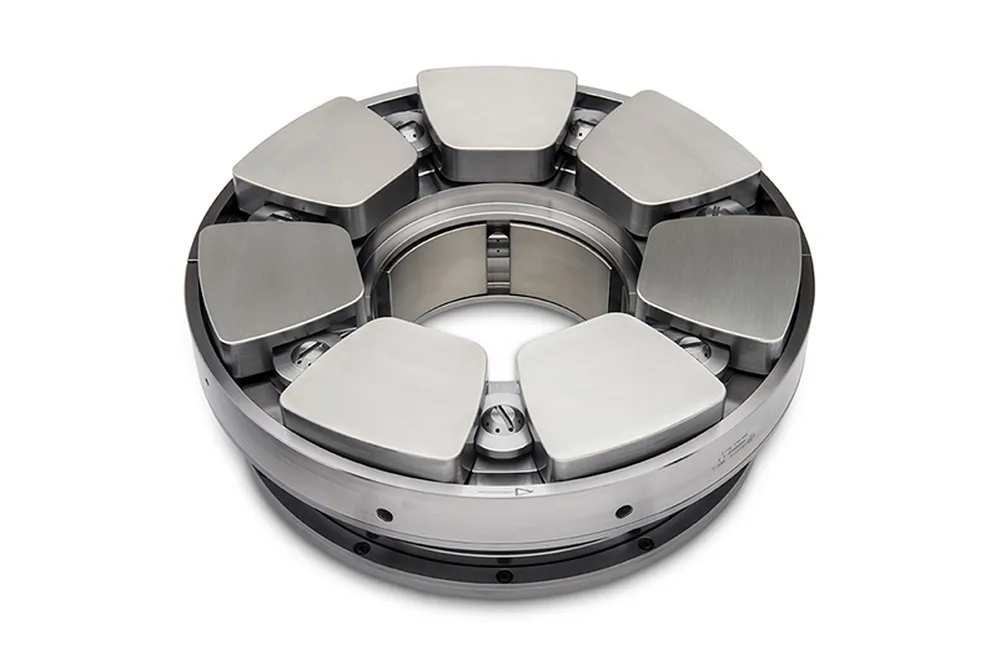

Main product model codes and parameter list
The following are some common radial fluid dynamic pressure bearing models and their parameters:
1. Cylindrical Plain Bearings
Model code: PJB-50×70, PJB-80×120
Parameters:
- Inner diameter (ID): 50 mm, 80 mm
- Outer diameter (OD): 70 mm, 120 mm
- Width (W): 50 mm, 80 mm
- Load capacity: 10 kN, 30 kN
- Speed range: 500-3000 rpm
- Lubrication method: self-lubrication or forced lubrication
- Material: Babbitt alloy or bronze
2. Elliptical Plain Bearing
Model code: EJB-60×90, EJB-100×150
Parameters:
- Inner diameter (ID): 60 mm, 100 mm
- Outer diameter (OD): 90 mm, 150 mm
- Width (W): 60 mm, 100 mm
- Load capacity: 20 kN, 50 kN
- Speed range: 1000-5000 rpm
- Lubrication method: forced lubrication
- Material: Babbitt alloy
3. Multi-lobe Plain Bearing
Model code: MLB-70×100, MLB-120×180
Parameters:
- Inner diameter (ID): 70 mm, 120 mm
- Outer diameter (OD): 100 mm, 180 mm
- Width (W): 70 mm, 120 mm
- Load capacity: 30 kN, 80 kN
- Speed range: 2000-8000 rpm
- Lubrication method: forced lubrication
- Material: bronze or polymer composite material
4. Tilting Pad Plain Bearing
Model code: TPB-80×120, TPB-150×200
Parameters:
- Inner diameter (ID): 80 mm, 150 mm
- Outer diameter (OD): 120 mm, 200 mm
- Width (W): 80 mm, 150 mm
- Load capacity: 50 kN, 100 kN
- Speed range: 3000-12000 rpm
- Lubrication method: forced lubrication
- Material: Babbitt alloy or special coating
Application analysis
Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing is widely used in the following fields:
Industrial equipment:
- Application scenarios: motors, pumps, compressors, fans, etc.
- Features: strong load capacity, stable operation, long life.
Energy industry:
- Application scenarios: turbines, steam turbines, gas turbines, etc.
- Features: adapt to high-speed and heavy-load conditions, high reliability.
Transportation:
- Application scenarios: ship propulsion shafts, railway locomotive shafts, etc.
- Features: impact resistance, vibration resistance, adapt to complex working conditions.
Precision machinery:
- Application scenarios: machine tool spindles, precision instruments, etc.
- Features: high precision, low friction, stable operation.

FAQ
Q1: What are the advantages of Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing compared with rolling bearings?
A1: Radial hydrodynamic bearings have higher load capacity, better damping characteristics and longer service life, and are particularly suitable for high-speed, heavy-load and continuous operation. In addition, hydrodynamic bearings are quieter during operation and do not require frequent maintenance.
Q2: How to choose a suitable Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing?
A2: The following factors should be considered when selecting:
- Load size and direction.
- Operating speed range.
- Lubrication method and lubricant type.
- Working environment (temperature, humidity, pollution, etc.).
- Installation space and structural limitations.
Q3: What are the lubrication methods of Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing?
A3: Common lubrication methods include:
- Self-lubrication: Automatically form a lubricating film by rotating the journal.
- Forced lubrication: Force the lubricating oil through an external oil pump.
- Oil ring lubrication: Use oil rings to bring the lubricating oil to the bearing surface.
Q4: What are the common faults of Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing?
A4: Common faults include:
- Insufficient lubrication causes wear or burning of bearings.
- Lubricant contamination causes bearing damage.
- Improper installation causes eccentric wear or vibration of bearings.
- Overload or overheating causes bearing failure.
Q5: How to maintain Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing?
A5: Maintenance measures include:
- Regularly check the quality and oil level of lubricating oil.
- Clean the lubrication system to prevent contamination.
- Monitor bearing temperature and vibration.
- Regularly replace worn bearing bushings or adjust clearances.
Radial Hydrodynamic Bearing occupies an important position in industrial equipment due to its excellent performance and wide range of applications. Correct selection, installation and maintenance are the key to ensure its long-term stable operation.



